TB 43-0213
2-4.
Arresting Rust/Repairing Rust Dam-
conditions and corrosion deposits present are similar to
age.
Stage 2 except that metal in corroded area is unsound,
and small pin holes may be present.
a. Stage 1 and Stage 2 rust can be readily repaired.
With Stage 3 rust, the metal is unbound and must be
cleared of rust and then reinforced, or the affected part
must be replaced entirely. Areas showing Stage 4 rust
are not repairable. Such parts must be replaced.
b. Rust in Stages 1 and 2 can be removed by use of
an abrasive such as a sander, grinder, or wire brush,
and/or by application of a rust removing compound.
The best approach taken to remove rust depends
greatly on the area being repaired as well as by such
considerations as metal thickness or accessibility of the
rusted area. A metal grinder, for example, would be
incorrect for use on thin, short metal. Interior rust in
long boxed-in areas close to rubber molding (such as
the tube rails of a fold-down window) may require use
of a wipe-off rust remover and swab as opposed to a
wash-off rust remover. Common sense and an
understanding of the tools and materials available must
determine the best approach.
c. Whenever rust is located on a vehicle that cannot
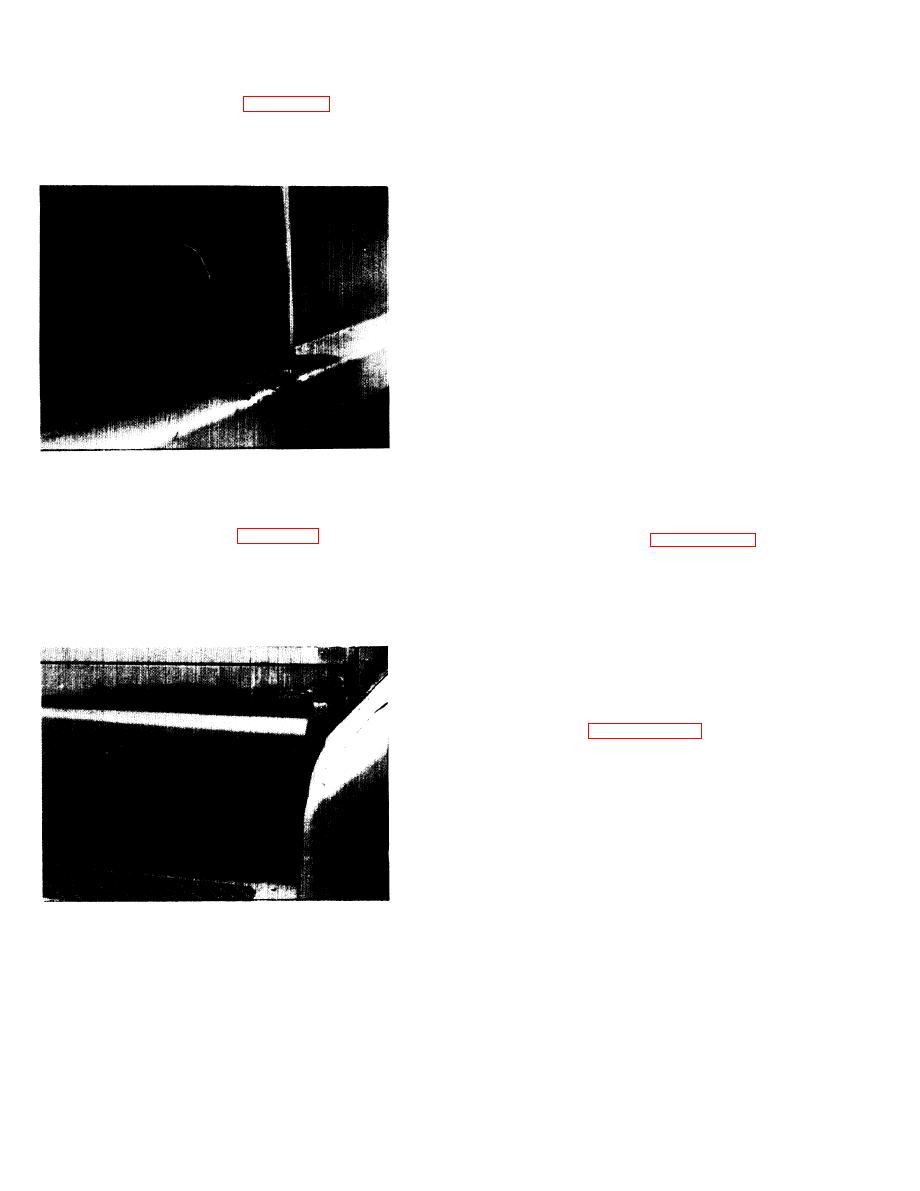
TA504745
Figure 2-4. Stage 3 Rust.
be immediately repaired, the rust area should at least be
treated with rust arresting coating, MIL-R-10036, to
(4) Stage 4 Rust (see Figure 2-5), Corrosion
prevent further corrosion. Refer to paragraph 2-20 for a
has advanced to the point where the metal has been
description of this material, its application, and
penetrated throughout. No metal remains at the point
hazards.
of severest corrosion. There are holes in the surface
d. Most Stage 1 and Stage 2 rust is localized and can
area or metal is completely missing along the edges.
be easily removed. Larger areas may require use of high
pressure washers. If repair is to be done immediately,
application of the rust arresting coating (MIL-R-10036)
is not necessary. Sand, grind, brush, and/or chemically
remove the rust from the metal. Maintenance
personnel should be aware of all chemical materials
available to assist in removing rust as well as any oils or
chemicals on the metal. Paragraphs 2-19 through 2-28
provide a list of these materials.
e. Stage 2 and Stage 3 rust are very similar in
appearance. What qualifies rust as Stage 3 depends to a
great degree upon the thickness of the metal. Rust
could appear as more advanced on the heavy-gaged
metal of a cargo or dump body and yet be categorized
as Stage 2. What may appear as minor rust on sheet
metal may be Stage 3. The difference is in the
soundness of the metal. Inspectors looking at the first
example of the cargo or dump body may determine by
probing and sounding that the metal beneath the rust is
still sound. Such rust would be classified as Stage 2.
TA504746
These same inspectors may determine that the less
Figure 2-5. Stage 4 Rust.
visible rust on the sheet metal has made that metal
b. Stages of rust are determined by visual inspection
unbound `or unserviceable. The sheet metal rust,
as well as by knocking on the metal to determine metal
therefore, would be categorized as Stage 3.
soundness. Probes, spring-loaded punches, or similar
f. Stage 3 and Stage 4 rust make the rusted part
devices should be used if the soundness of the metal is
unserviceable. Repairing rust damage in such cases
in doubt.
2-4


